How Windows Server Works & Which License You Should Get
Powering the backbone of many businesses, Windows Server is a Microsoft-developed operating system designed for robust enterprise management. This post aims to unravel the intricacies of Windows Server, from its key operational features to the ins and outs of its licensing.
Core Components of Windows Server
Active Directory (AD)
Active Directory is a database that keeps track of all the users, groups, and computers within a network. It acts as the gatekeeper, managing permissions and access to network resources. Notably, it uses Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) for querying and modifying items and Kerberos for secure authentication.
AD organizes all network objects into a hierarchical structure, which eases navigation and search operations. It supports policy enforcement and scripting capabilities, allowing automation of regular administrative tasks.
For instance, a network admin could set up a policy that applies specific security settings to all devices in an organizational unit or send software updates to all users within a specific group.
File and Storage Services
Windows Server’s File and Storage Services provide a wide array of features for data management. Network file sharing enables users within a network to share and collaborate on files efficiently. It supports SMB (Server Message Block) and NFS (Network File System) protocols, catering to Windows and non-Windows clients.
Data deduplication is a feature that eliminates duplicate copies of repeating data, effectively saving storage space. Meanwhile, the storage tiering feature automatically moves frequently accessed data to faster storage and infrequently accessed data to slower storage, optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness.
For example, a business could save significant storage space by utilizing data deduplication for their document archives, where multiple versions of similar documents may exist.
Web and Application Servers
Windows Server includes Internet Information Services (IIS), a versatile and extensible web server. It supports HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, and SMTP, allowing for various web-based applications and services.
Beyond hosting websites, IIS is capable of hosting web services and applications, offering support for ASP.NET, PHP, and other popular frameworks. This functionality is integral to many business operations, as it provides a platform for deploying enterprise-level applications.
For instance, a company could host its internal portal, content management system, and API backend on a Windows Server running IIS.
Virtualization with Hyper-V
Hyper-V in Windows Server enables the creation of virtual machines (VMs), each with its own isolated operating system and resources. This means a single physical server can run multiple operating systems simultaneously, each within its own virtual environment.
Virtualization allows businesses to maximize hardware utilization and reduce costs. It provides flexibility and scalability, as VMs can be created, deleted, or modified easily without requiring new physical equipment.
For instance, a software development company could use Hyper-V to create different VMs for testing their applications on various operating systems without needing separate hardware for each.
GUI and PowerShell Management
Windows Server offers both a GUI and PowerShell for administration, catering to various user preferences and needs. The GUI, known as Server Manager, provides an intuitive and visual way to manage roles, features, and other server settings.
On the other hand, PowerShell is a command-line tool and scripting language, providing a more powerful and flexible way to manage Windows Server. With PowerShell, administrators can automate complex and repetitive tasks, streamline processes, and access detailed system information that isn’t readily available through the GUI.
For example, an admin could use PowerShell to automate the creation of new user accounts from a list, a task that would be time-consuming through the GUI.
Navigating the Licensing Landscape
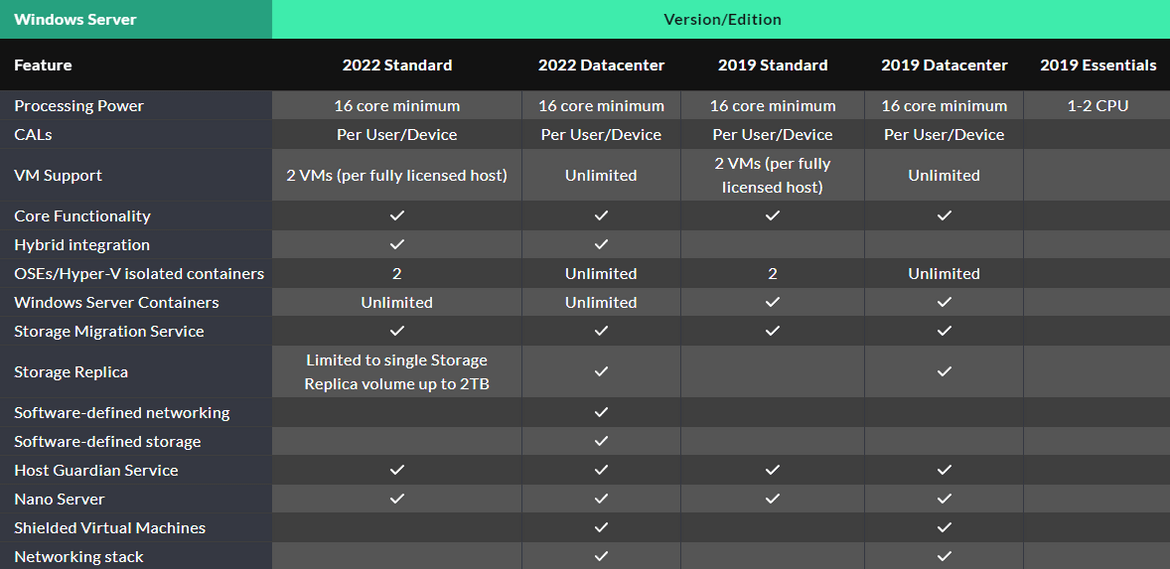
The licensing structure for Windows Server is primarily based on a core-based model. Here are the three main editions of Windows Server, explained with real-world scenarios to provide a clearer understanding:
-
Standard Edition: The Standard Edition is the go-to option for non-virtualized or lightly virtualized environments. Each license must cover a minimum of 16 Cores per physical server. This makes it a viable choice for small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) that have a few key applications they need to run on separate virtual machines for improved reliability.
Example Scenario: Consider an SMB that runs a customer relationship management (CRM) system and accounting software. They could have one virtual machine dedicated to each, isolating these critical applications from each other. If they’re running these on a dual-processor server meeting the 16 Core licenses, a single Standard Edition license will suffice.
-
Datacenter Edition: The Datacenter Edition is tailored for highly virtualized environments, including data centers and cloud setups with specific licensing models. Each license covers one host but allows for unlimited virtual machines. This makes it an economical choice for large enterprises or service providers with heavy virtualization needs.
Example Scenario: A cloud service provider hosts a plethora of applications for various clients. They might run hundreds of virtual machines on a single multi-core server to efficiently use their hardware resources. In this case, the Datacenter Edition would be their most cost-effective licensing option, as it allows for unlimited virtualization.
-
Essentials Edition: The Essentials Edition is crafted for small businesses with up to 25 users and 50 devices. It offers features like file and print sharing and data backup. This edition does not support virtualization, making it a streamlined and cost-effective solution for small businesses that need essential services without the complexities of managing virtual machines.
Example Scenario: A local retail business with 20 employees uses a single server for file sharing, managing its inventory system, and running its point-of-sale (POS) system. They do not need virtualization and only have a single, dual-core processor server. The Essentials Edition would provide all the features they need cost-effectively.
It’s important to remember that only “Standard and Datacenter” require Client Access Licenses (CALs) for every user or device accessing the server. Furthermore, users or devices accessing the server that requires Remote Desktop Services (RDS) features of Windows Server require RDS CALs on top of the CALs. By understanding your business needs and planning your server deployments effectively, you can ensure that you choose the most cost-effective and suitable Windows Server edition and licensing structure.
Security and Compliance
Windows Server features robust security features like BitLocker for disk encryption, Windows Defender for threat detection, and advanced auditing capabilities to ensure resilience against potential security threats.
Windows Server is a comprehensive tool designed to meet diverse and complex business needs. Understanding both the functional and licensing aspects of Windows Server is vital to leverage its full potential. Microsoft continues to innovate its server operating systems to empower businesses to meet their objectives efficiently and securely.
Stay tuned as we explore more features and capabilities of Windows Server in our future posts, aimed to empower you with insights to optimize your IT infrastructure.
Trusted Tech Team is an accredited Microsoft CSP Direct Bill Partner, carrying multiple Solutions Partner designations and the now-legacy Microsoft Gold Partner competency. Based in Irvine, California, we report trends affecting IT pros everywhere.
If your organization uses Microsoft 365 or Azure, you may be eligible to receive a complimentary savings report from a Trusted Tech Team Licensing Engineer. Click here to schedule a consultation with our team now to learn how much you can save today.
Subscribe to the Trusted Tech Team Blog
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox