Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Affecting Exchange Server
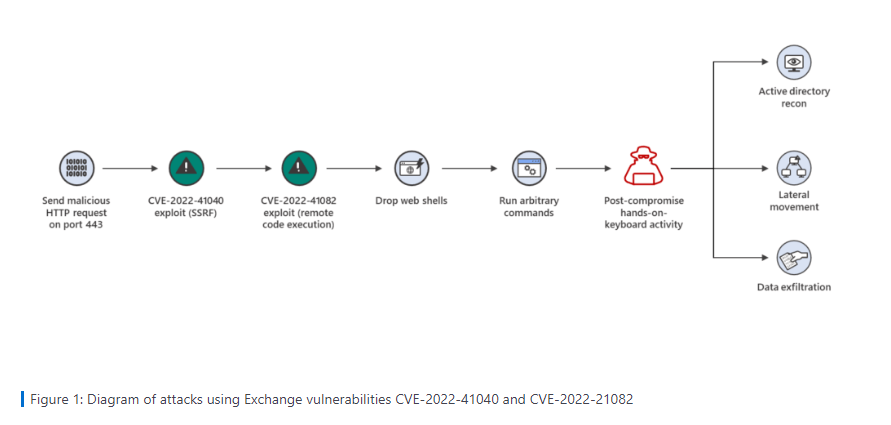
In a blog post on Thursday, September 29th, Microsoft announced that they are investigating two zero-day vulnerabilities that attackers were able to exploit to gain remote access to Microsoft Exchange Server: CVE-2022-41040, which is a server-side request forgery (SSRF), and CVE-2022-41082, which permits remote code execution (RCE) when Exchange PowerShell is accessible to the attacker.
In response, Microsoft has put together mitigation measures to help affected systems intercept potential attacks. Although these measures are not sufficient to protect on-premises servers, Microsoft recommends that admins of on-premises servers implement them to maximize protection against possible attacks. At the time of publishing this post, Microsoft had recorded 10 attacks globally.
Activities in the Wild
GTSC has recorded attacks that created backdoors on Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, 2016, and 2019 - and performed lateral movements to other servers in the systems. “We detected webshells, mostly obfuscated, being dropped to Exchange servers. Using the user-agent, we detected that the attacker uses Antsword, an active Chinese-based opensource cross-platform website administration tool that supports webshell management.”, the GTSC team added.
Although Microsoft stated that these attacks require authenticated access, it is important to note that any standard user credential can be obtained relatively easily by common attack methods.
Summary of Microsoft’s Mitigation Steps
Microsoft Exchange Server customers using Microsoft 365 Defender are advised to follow this checklist:
- Turn on cloud-delivered protection in Microsoft Defender Antivirus
- Turn on tamper protection features
- Run EDR in block mode
- Enable network protection
- Enable investigation and remediation in full automated mode
- Use device discovery to increase your visibility into your network
See full mitigation steps here. No action is required for Microsoft Exchange Online since it is not affected by these vulnerabilities.
How to Protect On-premises Servers
The steps above do not provide full protection for on-premises servers. Therefore, admins are advised to review and apply Microsoft’s URL Rewrite Instructions. Alternatively, admins may run Microsoft’s updated Exchange On-premises Mitigation Tool which will apply the URL rewrite mitigation. System requirements and full instructions are available here.
One important caveat is that the rule that Microsoft suggests only protects against known attacks. Therefore, admins are strongly advised to maintain the highest security practices until Microsoft releases a patch.
Trusted Tech Team is an accredited Microsoft CSP Direct Bill Partner, carrying multiple Solutions Partner designations and the now-legacy Microsoft Gold Partner competency. Based in Irvine, California, we report trends affecting IT pros everywhere.
If your organization uses Microsoft 365 or Azure, you may be eligible to receive a complimentary savings report from a Trusted Tech Team Licensing Engineer. Click here to schedule a consultation with our team now to learn how much you can save today.
Subscribe to the Trusted Tech Team Blog
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox