The Blockchain Consensus
Though blockchain is most commonly associated with cryptocurrency, it actually debuted nearly two decades before the crypto phenomenon began.
Blockchain was originally conceived as a preventive measure against document timestamp tampering, as each blockchain node/participant maintains a replica of a shared ledger of digitally signed transactions. Over time, blockchain has evolved into a decentralized coordination mechanism for consensus-based organizational structures.
Consensus Algorithms
A consensus algorithm is the multinodal process of validating and ensuring transacted data is correctly recorded into a block and replicated to other nodes. It assures that protocol rules are followed while guaranteeing that all transactions occur in a trustless way (i.e., coins are singularly spent). The most common consensus implementations are PoW and PoS, each of which balances security, functionality, and scalability:
Proof of Work (PoW)
PoW is a consensus algorithm that is essential to cryptomining and employed by Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, etc. It ensures miners only validate a new transaction block and add it to the blockchain when network distributed nodes consensualize the miner-provided block hash as a valid proof of work. PoW is a top solution to the Byzantine Generals’ Problem, which made for the creation of Bitcoin as a “Byzantine Fault Tolerant” system.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
PoS replaces PoW mining with a more economic and energy-efficient mechanism that validates blocks by participant stake. The validator (forger or minter) of each block is determined via cryptocurrency investment or allocated computational power. The blockchain (e.g., Decred, Peercoin, Ethereum) is secured by an election process contingent upon node wealth, coin age (i.e., length of time coins are locked or staked), and randomization.
Other consensus formats include:
- Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) – allows token holders vote to elect delegates to validate tokens on their behalf
- Decentralized Asynchronous Proof of Stake (DAPoS) – enables massive data transfers and enterprise-scale applications
Applied Algorithms
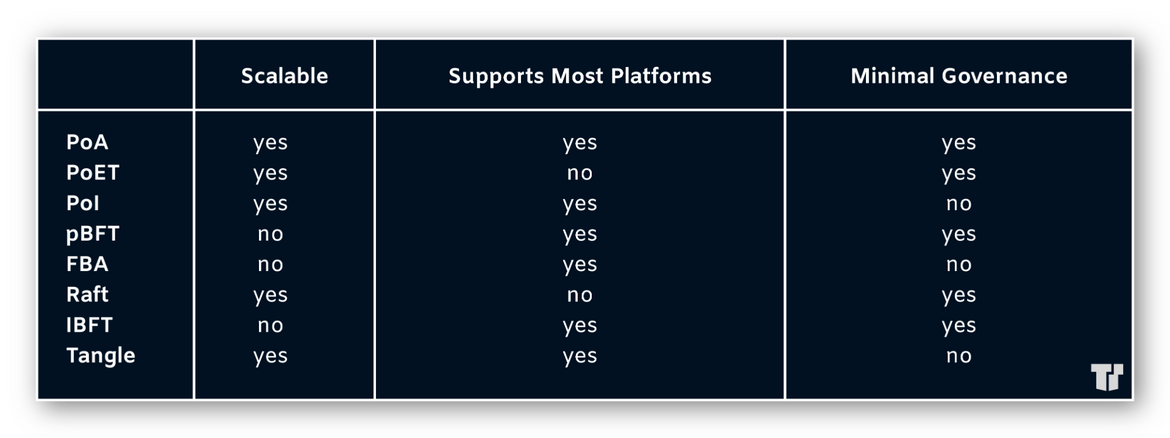
Each consensus algorithm is applicable to a specific use case, which can be determined by the following criteria:
- Scalable — ranges from small participants to multiple nodes
- Platform supportive — unrestricted by specific hardware
- Minimal governance — system requires limited human input
When considering the consensus algorithm best suited to a specific product or service, consider its mathematical and decision-making architectures to maintain masternode multifunctionality in a secure and decentralized manner. Balance blockchain speed and stability within minimal active nodes while considering internal economy logic, thus encouraging fair play amongs masternode holders.
Trusted Tech Team is an accredited Microsoft CSP Direct Bill Partner, carrying multiple Solutions Partner designations and the now-legacy Microsoft Gold Partner competency. Based in Irvine, California, we report trends affecting IT pros everywhere.
If your organization uses Microsoft 365 or Azure, you may be eligible to receive a complimentary savings report from a Trusted Tech Team Licensing Engineer. Click here to schedule a consultation with our team now to learn how much you can save today.
Subscribe to the Trusted Tech Team Blog
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox

